| CAS
NO. |
87-33-2 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
201-740-9 |
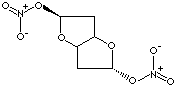
| FORMULA |
C6H8N2O8 |
| MOL
WT. |
236.14 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
3003.90
|
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
1,4:3,6-Dianhydro-D-glucitol dinitrate; |
| Dinitrato de isosorbida;
Dinitrate d'isosorbide; |
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white
crystalline powder |
| MELTING POINT |
69
C |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions. Hygroscopic. |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
|
Isosorbide is a bicyclic ether derivative of glucitol. The nitric acid esters of
isosorbide are used as osmotic diuretic to reduce intraocular pressure with
effects on both arteries and veins and to treat coronary insufficiency and
angina pectoris. The monoester is a white crystalline powder; melting point 140
C; freely soluble in water, alcohol and chloroform. The diester is a white
crystalline powder; melting point 70 C; sparingly soluble in water; soluble in
organic solvents (acetone, alcohol, ether); administered sublingually and orally. Eesters
are explosive. It should be diluted (25 -
40%) with lactose or mannitol for transportation.
Chemical designation is 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-D-glucitol mono (di) nitrate. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION (USP) |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white
crystalline powder |
|
PURITY
|
98.0%
min (Lactose 60% - 75%)
|
|
MELTING POINT |
69
C
|
|
SULFATED
ASH
|
0.1%
max
|
|
HEAVY
METALS
|
20ppm
max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kgs
in Drum |
| HAZARD CLASS |
4.1
(Packing Group: II) |
| UN
NO. |
2907 |
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 5-22, Safety Phrases:
36 |
